The Difference Between Mechanical, Thermal, and Electrical Properties of Engineering Plastics
- Mechanical Properties: Strength, toughness, and wear resistance are key factors in the mechanical performance of engineering plastics, making them ideal for structural applications.
- Thermal Properties: Engineering plastics exhibit high heat resistance and thermal stability, which are crucial for applications involving high-temperature environments.
- Electrical Properties: The electrical insulation capabilities of engineering plastics are essential in electronics and electrical applications, where safety and performance are paramount.
Engineering plastics play a pivotal role in modern manufacturing, offering superior performance characteristics over conventional plastics. These materials are not only known for their exceptional durability but also for their specialised properties that make them suitable for a wide range of applications. In this article, we will delve into the critical differences between the mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties of engineering plastics.
We will provide a comprehensive understanding of how these properties influence material selection in various industries, including the booming market for engineering plastics in Australia.
Engineering plastics are a subset of plastic materials that offer superior mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties compared to standard plastics. These materials are typically thermoplastics, which means they can be moulded and remoulded into complex shapes while maintaining their performance characteristics. This flexibility in processing, combined with their enhanced properties, makes engineering plastics the material of choice for demanding applications across industries such as automotive, electronics, aerospace, and medical devices.
Unlike standard plastics, engineering plastics are often custom-engineered to meet the specific requirements of an application. This ability to tailor properties such as strength, heat resistance, and electrical insulation allows manufacturers to optimise performance and ensure the longevity of their products. For instance, PEEK plastic is often selected for applications that demand exceptional thermal stability and chemical resistance.
Mechanical Properties of Engineering Plastics
-
Strength and Toughness
One of the most important mechanical properties of engineering plastics is their strength, which refers to the material's ability to withstand an applied force without breaking. Strength is crucial in applications where the plastic will be subjected to heavy loads or impacts. For instance, polycarbonate sheets are renowned for their high impact resistance and strength, making them an ideal material for safety helmets and protective glazing.
Toughness, on the other hand, is a measure of a material's ability to absorb energy and plastically deform without fracturing. Engineering plastics like Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) exhibit excellent toughness, which is why they are widely used in applications requiring durability, such as automotive interiors and consumer electronics.
-
Wear Resistance
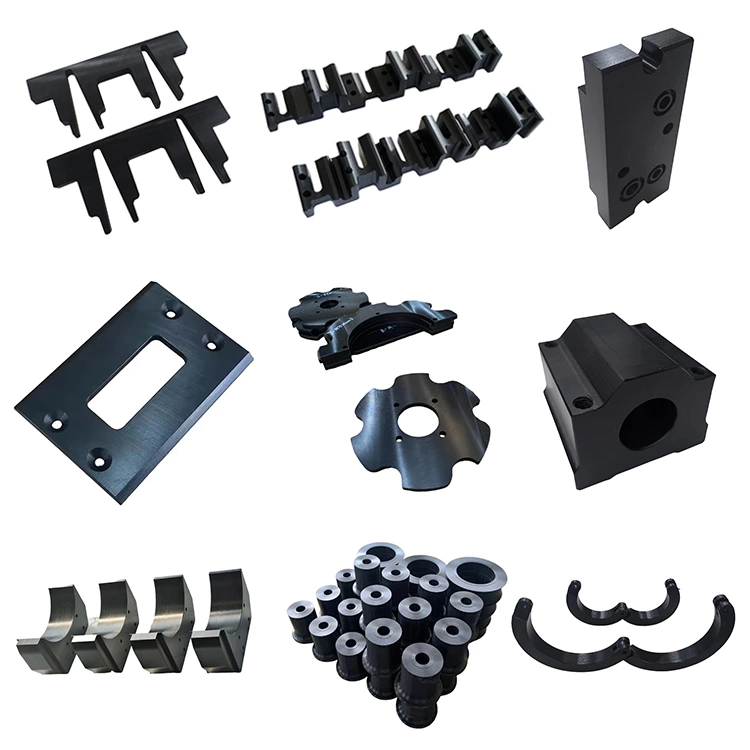
Wear resistance is another critical mechanical property, particularly in applications involving moving parts that are subject to friction. Engineering plastics such as acetal plastic products and UHMWPE plastic are highly valued for their low friction coefficients and good wear resistance. Acetal plastic products, also known as POM, are often used in gears, bearings, and other components where long-term durability and smooth operation are essential.
-
Dimensional Stability
Dimensional stability refers to the ability of a material to maintain its size and shape under varying environmental conditions, such as changes in temperature and humidity. Engineering plastics like cast nylon sheets and PTFE plastic are prized for their excellent dimensional stability. This property is particularly important in precision applications, such as in the manufacture of mechanical parts where exact dimensions are critical to the product's performance.
Thermal Properties of Engineering Plastics
-
Heat Resistance
Thermal properties are crucial in determining how a material behaves under high-temperature conditions. Engineering plastics are often chosen for applications where heat resistance is required. PEEK plastic, for example, can withstand continuous use at temperatures as high as 260°C, making it suitable for demanding environments such as aerospace components and high-performance automotive parts.
-
Thermal Stability
Thermal stability is the ability of a plastic to retain its mechanical properties at elevated temperatures. Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) is a prime example of engineering plastic with outstanding thermal stability. PPS maintains its strength, hardness, and dimensional stability at temperatures up to 260°C, which is why it is often used in applications like electronic components and automotive engine parts that are exposed to high heat.
-
Thermal Conductivity
While most plastics are poor conductors of heat, certain engineering plastics are designed to have higher thermal conductivity for specific applications. For instance, PET plastic and Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) are often used in the electronics industry where controlled heat dissipation is necessary, such as in connectors and housings that must manage the heat generated by electrical components.
Electrical Properties of Engineering Plastics
-
Electrical Insulation
The ability to insulate against electricity is one of the most valuable properties of engineering plastics in electrical and electronic applications. Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO), for instance, is widely used for its excellent electrical insulating properties, which make it suitable for components such as electrical housings, circuit boards, and connectors.
-
Dielectric Strength
Dielectric strength is a measure of a material's ability to withstand electric stress without breaking down. Polypropylene (PP) and PET plastic are commonly used in applications requiring high dielectric strength, such as in capacitors and insulating films. These materials prevent electrical breakdown and ensure the reliability and safety of electronic devices.
-
Resistance to Electrical Tracking
Electrical tracking is the formation of a conductive path across the surface of an insulating material, which can lead to electrical failure. Engineering plastics like High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) are formulated to resist tracking, making them ideal for use in electrical insulators, switchgear, and other high-voltage applications.
The Interplay of Mechanical, Thermal, and Electrical Properties
In many applications, engineering plastics must meet stringent requirements across all three property categories—mechanical, thermal, and electrical. For example, automotive components must be strong and tough enough to withstand mechanical stresses, heat-resistant enough to endure engine temperatures, and electrically insulating sufficient to prevent short circuits and ensure safety.
Similarly, in the electronics industry, materials must combine high dielectric strength, excellent dimensional stability, and heat resistance to ensure reliable performance over time. This interplay of properties underscores the importance of selecting the right engineering plastic for a given application.
In engineering plastics markets in Australia, materials such as HDPE sheets and polycarbonate sheets are often chosen for their balance of mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties.